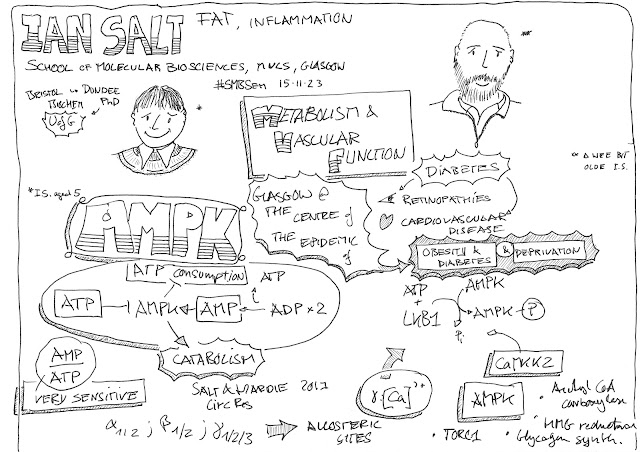
Ian Salt, School of Molecular Biosciences, University of Glasgow:
Fat, Inflammation and AMP activated Protein Kinase
15.11.2023 Part of the School of Molecular Biosciences Seminar Series, Organised & Hosted by Brian Hudson
Papers mentioned in the talk:
Salt, I. P. and Hardie, G. (2017) AMP-activated protein kinase: an ubiquitous signalling pathway with key roles in the cardiovascular system. Circulation Research, 120(11), pp. 1825-1841.
Palmer, T. M. and Salt, I. P. (2021) Nutrient regulation of inflammatory signalling in obesity and vascular disease. Clinical Science, 135(13), pp. 1563-1590.
Kopietz, F., Alshuweishi, Y., Bijland, S., Alghamdi, F., Degerman, E., Sakamoto, K., Salt, I. P. and Göransson, O. (2021) A-769662 inhibits adipocyte glucose uptake in an AMPK-independent manner. Biochemical Journal, 478(3), pp. 633-646.
Alghamdi, F., Alshuweishi, Y. and Salt, I. P. (2020) Regulation of nutrient uptake by AMP-activated protein kinase. Cellular Signalling, 76, 109807.
Mancini, S. J., Boyd, D., Katwan, O. J., Strembitska, A., Almabrouk, T. A., Kennedy, S. , Palmer, T. M. and Salt, I. P. (2018) Canagliflozin inhibits interleukin-1β-stimulated cytokine and chemokine secretion in vascular endothelial cells by AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Scientific Reports, 8, 5276.
Almabrouk, T. A. M. , Ugusman, A. B., Katwan, O. J., Salt, I. P. and Kennedy, S. (2017) Deletion of AMPKα1 attenuates the anticontractile effect of perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) and reduces adiponectin release. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(20), pp. 3398-3410.